Table of contents
What does a while loop do?
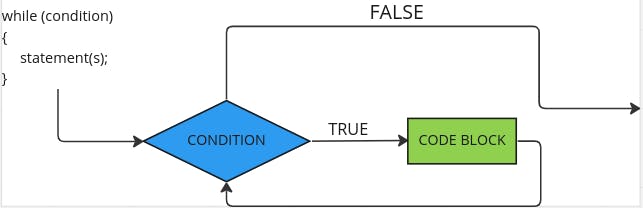
A while loop repeatedly executes a target statement as long as a given condition is TRUE. In this context, a statement is a unit of code that performs a pre-determined task.
Syntax:
while (condition)
{
statement(s);
// statements have to be true for the code block to run
}
In the above example, statement(s);, is a single statement or a block of statements.
The (condition) is any expression, and true is any other value other than zero0.
The loop repeats while the (condition) is true.
Also, the statement(s); need to be updated, i.e incremented or decremented. Otherwise, the loop will run infinitely as the statement(s); will always return a value that's true.
When the condition becomes false, the program control passes to the statement immediately following the loop. Basically, the loop stops.
Sample Code:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(void)
{
int x = 0;
while (x < 12) //while (condition)
{
printf("%d \n", x); //(statement); -prints an integer if condition is true
x++; //(updation); -increments the integer
}
return(0);
}
